
BBUGSS
British Benign
Upper Gastrointestinal
Surgical Society
_edited_edited.png)
Partner of AUGIS
LINX Guidelines (NICE)
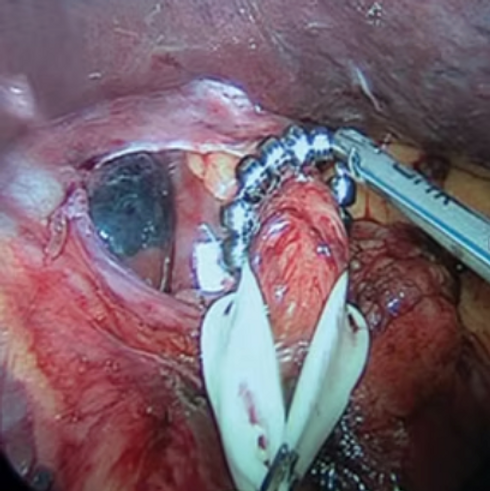
Anti-Reflux Surgery (Magnetic Sphincter Augmentation/LINX) Recommendations
Definition:
Non-anatomical altering, life style anti-reflux surgery with or without synchronous hiatus hernia repair with the use of magnetic bead prosthetic implant
Recommendations:
-
LINX is a valid alternative to fundoplication in selected patients with symptomatic reflux with equivalent outcomes and safety
-
Anti-Reflux surgeons should be aware of LINX outcomes and limitations compared to fundoplication and advise patients appropriately if asked
-
LINX providers should have received appropriate training and mentorship (Completion of 2-day industry In-Hospital Training program (Virtual) with expert LINX surgeons)
-
Criteria for surgeons training in LINX:
-
Performing anti-reflux and foregut surgeries regularly.
-
Performing a minimum of 10 laparoscopic fundoplication procedures (over the last 12 months).
-
Access & experience in pre-operative diagnostic work-up including OGD, pH monitoring, Manometry & Barium contrast study.
-
Works in collaboration with GI physician and multi-disciplinary team
-
-
LINX providers should be performing >10 procedures per year
-
LINX should be offered as an alternative option to fundoplication surgery in eligible patients
-
patients in whom the primary symptom is volume reflux/regurgitation
-
a confirmed diagnosis of acid reflux and adequate symptom control with medical therapy but do not wish to continue with long term therapy
-
patient with breakthrough symptoms despite maximum medical therapy
-
a confirmed diagnosis of acid reflux and symptoms that respond to medical therapy but who are intolerant of medication side effects
-
atypical symptoms such as aspiration, cough or hoarse voice and confirmed evidence of GORD (these patients as a group have less successful outcomes than patients with typical symptoms)
-
-
As a minimum, complex/equivocal patients should be discussed at a hiatal MDT* prior to surgery, best practice to discuss all patients prior to surgery.
-
Enter data into a registry to audit outcomes
-
Not recommended with hiatal hernia > 3 cm (unless provider high volume/experienced)
-
Surgery not recommended with BMI >35
-
Surgery not recommended in age <21
-
Surgery not recommended in active smoker
-
Surgery not recommended with significant history of dysphagia
Investigations:
As a minimum, patients being considered for LINX should undergo
-
OGD
-
pH analysis
-
High Resolution Manometry- Mean contractile amplitude of >30 mm Hg in 70% of swallows is recommended prior to magnetic sphincter augmentation
-
Other investigations to consider in patients with additional upper gastrointestinal symptoms such as bloating, nausea, vomiting, and early satiety: Contrast swallow/gastric emptying study
-
Atypical symptoms: ENT or respiratory opinion sort pre-operatively
Key performance Indicators:
-
Laparoscopic conversion to open < 2%
-
Less than 24 stay for > 90%
-
Readmission rates within 30 days <5%
-
Re-operation rate within 30 days (acute complications) <2%
-
Re-operation for device herniation (within 1 year) <10%
-
Long term device erosion <1%
-
>80% of patients should not require regular anti-acid medication at 5 years after surgery
-
Morbidity <5%
-
Mortality < 0.1%
Please also see the European Foregut Society recommendations on sizing the LINX prosthesis.
https://euro-fs.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/Expert-ConsensusSizing.pdf

LINX Providers
Below are Upper Units that provide NHS LINX